Call us +44 1922 867 508
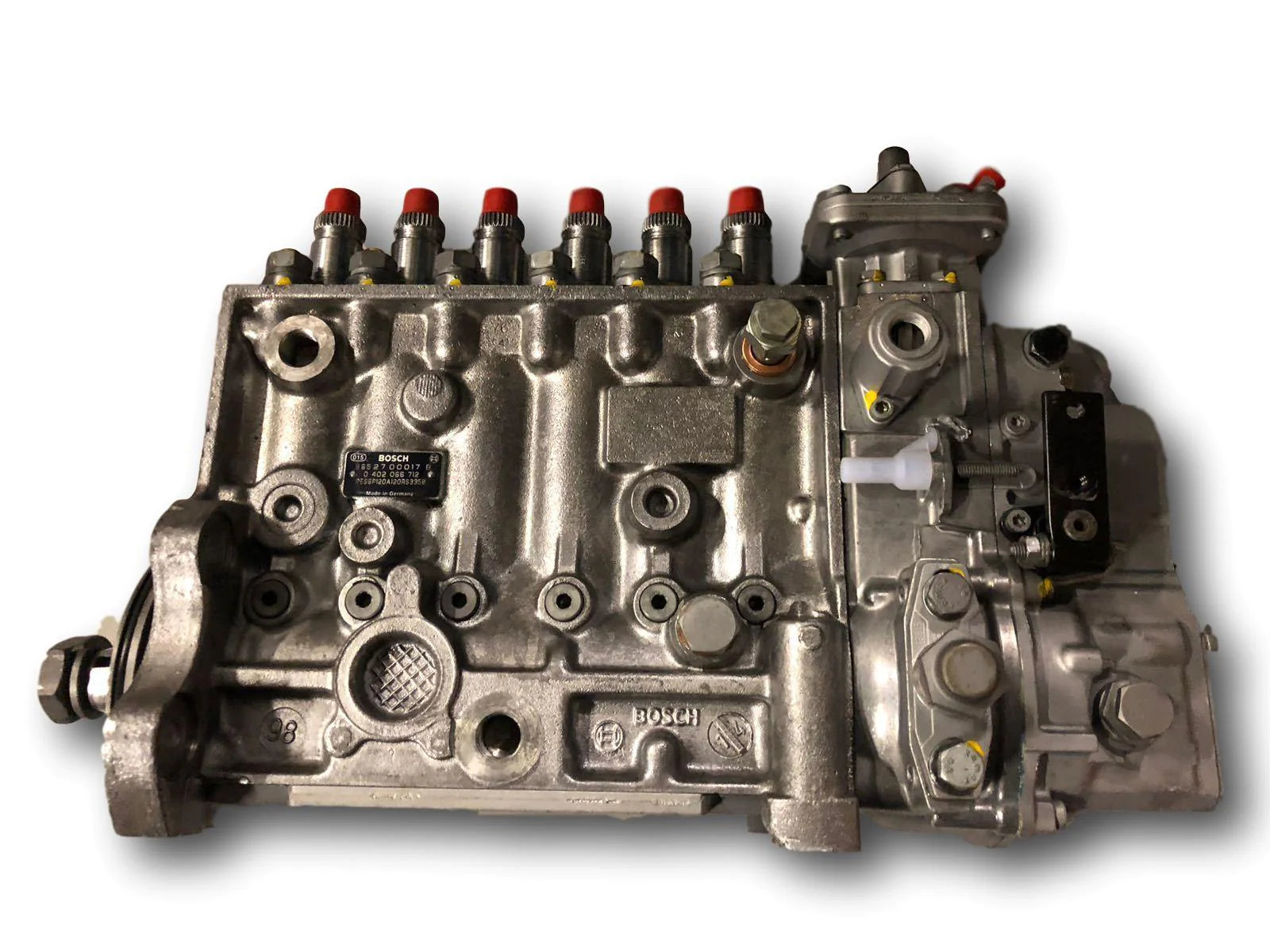
What is a In Line Diesel Injection Pump?
An inline diesel fuel injection pump is a type of fuel injection system used in diesel engines. It is also known as a distributor-type pump. This pump is a critical component responsible for delivering fuel to the individual injectors in the engine cylinders with precise timing. Inline pumps were widely used in older diesel engines and are still found in certain applications today, although they have largely been superseded by more advanced fuel injection systems like common rail.
Here are the key characteristics and workings of an inline diesel fuel injection pump:
-
Inline Configuration: The term "inline" refers to the configuration of the pump. In an inline pump, the fuel pump and injector system are arranged in a straight line, typically driven by the engine's camshaft.
-
Individual Pump Elements: The inline pump consists of individual pump elements, each dedicated to a specific engine cylinder. These pump elements are connected to the engine's camshaft, and as the camshaft rotates, it drives the pump elements to pressurize and deliver fuel.
-
Mechanical Operation: The operation of inline pumps is mechanical, with the movement of engine components, such as the camshaft, directly influencing the fuel injection process. The mechanical linkage between the engine components and the pump elements determines the timing and quantity of fuel delivered to each cylinder.
-
Timing and Metering: The timing and metering of fuel injection in an inline pump are closely linked to the engine's mechanical design. Adjustments to injection timing and quantity often require mechanical modifications to the pump.
-
Limited Flexibility: One limitation of inline pumps is their limited flexibility in adjusting fuel injection parameters. Changes in engine operating conditions may not be as easily accommodated compared to more modern fuel injection systems.
-
Used in Older Engines: Inline diesel fuel injection pumps were prevalent in older diesel engines and were known for their reliability. However, as engines evolved to demand more precise control over fuel delivery for improved efficiency and emissions control, more advanced systems like common rail injection gained prominence.
While inline diesel fuel injection pumps have been largely replaced by newer technologies in many applications, they still find use in specific industries or in certain types of engines where their simplicity and reliability are valued. Modern diesel engines often utilize electronic control systems and more advanced injection systems like common rail for improved performance and emissions control.
 Skip to content
Skip to content

